Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): The least expensive option which is primarily used for small parts and shipping trays. PVC has high chemical resistance, good stiffness and impact strength, and naturally flame retardant. Its properties do not work well for certain applications such as medical because of its relatively poor barrier against moisture ingress and oxygen ingress. Common industries and uses include: machine shops, work-in-progress trays, handling trays, consumer goods, display cases, marketing kits, blister packs, storage bins.
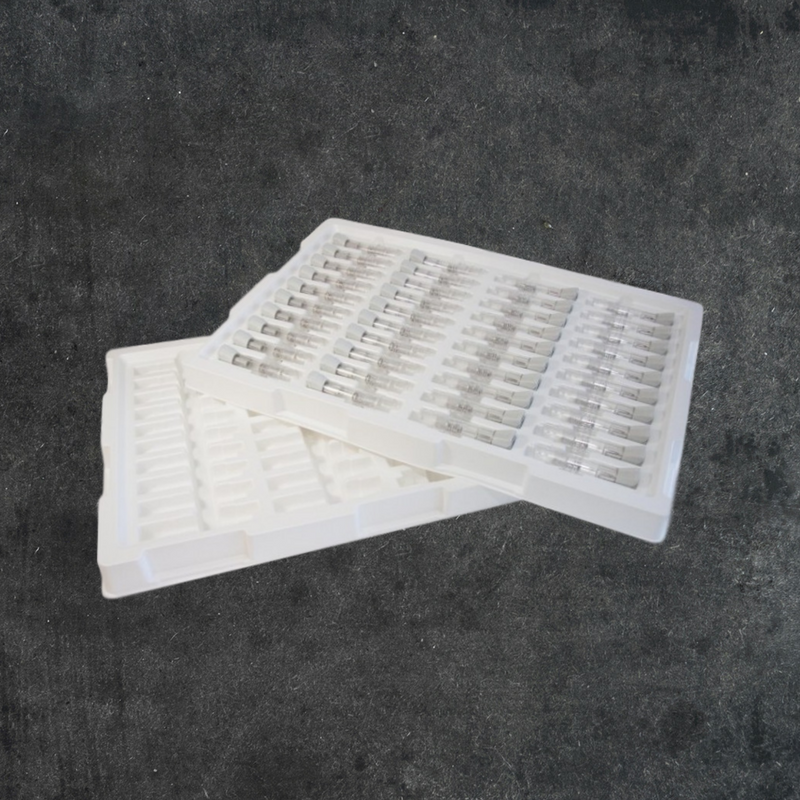
Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol (PETG): Great option for optics, medical trays, and other various medical applications. PETG comes in many different thickness options. This material has excellent strength, good clarity, chemical resistance, and overall outstanding thermoforming characteristics. Common industries and uses include: medical trays, medical clamshells, POP displays, signs, machine guards, consumer goods, electronics, display cases, marketing kits, blister packs.
Polystyrene (PS): Commonly used for disposable foodservice applications. PETG offers many great characteristics such as high chemical resistance, good clarity, easily moldable, inexpensive, and high electrical and heat resistance. Polystyrene is also easily recycled. One disadvantage of PS its low hardness and impact strength, meaning it can crack or break easier than other thermoform materials. Common industries and uses include: disposable cups, disposable applications, electrical application, POP displays, signs, electronics, foodservice applications, disposable shipping trays.
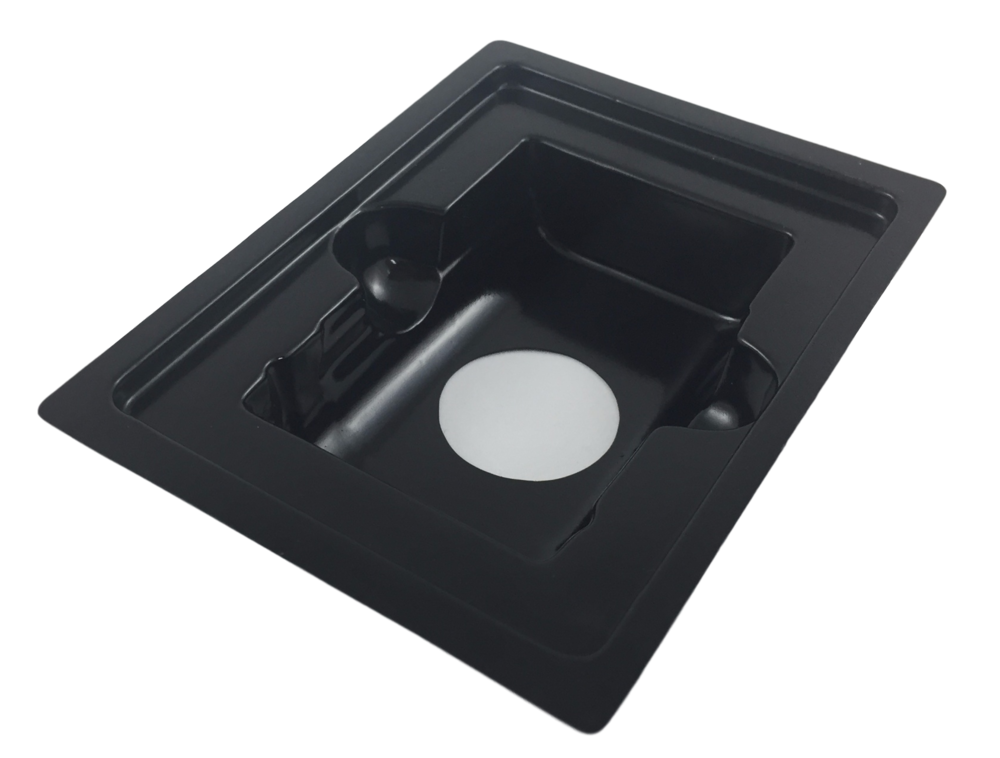
High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS): Compared to Polystyrene (PS), HIPS trades off the natural clarity offered by PS for greatly improved impact resistance and hardness. Similar to PS, HIPS has other advantages such as chemical resistance, dimensional stiffness, and moldability. HIPS is recyclable although the process is uneconomical. Common industries and uses include: consumer food containers, foodservice applications, POP displays, clamshell packaging, signs, consumer goods, bottles, shipping trays, reusable trays, picture frames.
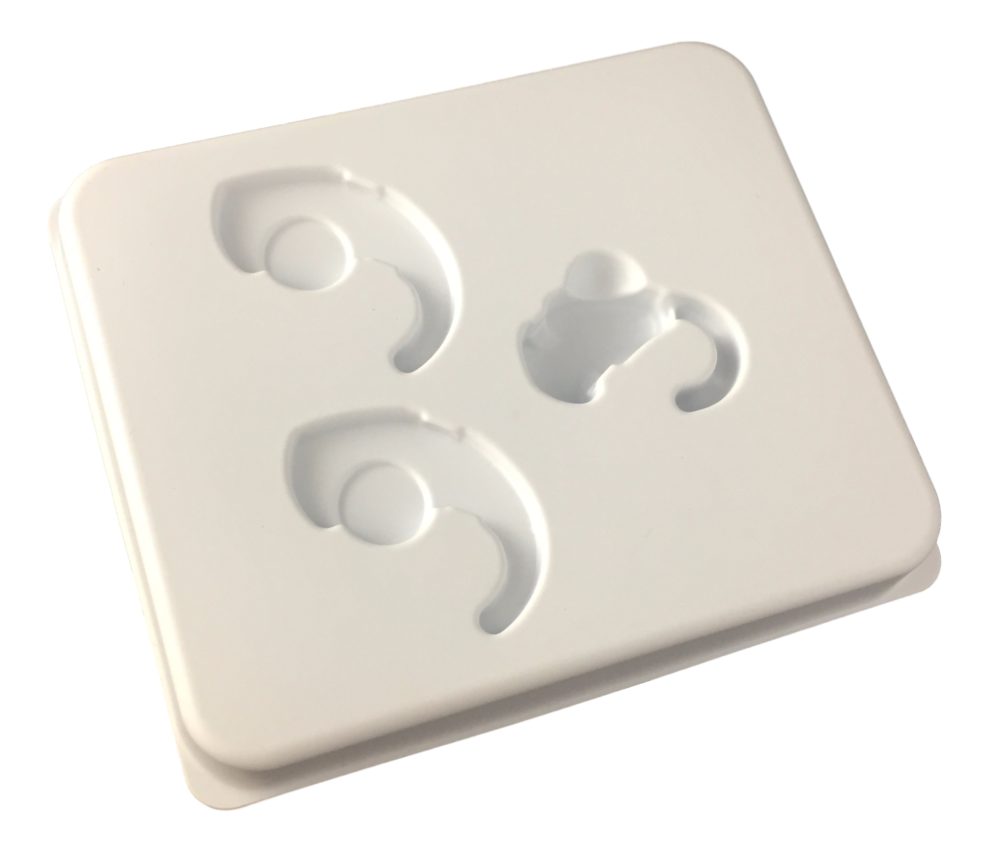
Polypropylene (PP): Commonly used for medical applications because of its unique chemical resistance properties and high heat deflection. Polypropylene material can withstand sterilization processes like autoclave. PP has a high level of stiffness but is not that hard making it susceptible to scratching or chipping. Common industries and uses include: medical trays, medical clamshells, dental trays, dental clamshells, food containers, consumer goods, shipping trays, storage trays.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): Engineered plastic that can have customized characteristics. ABS has good baseline impact strength, stiffness, and hardness as well as other beneficial properties such as heat deflection. It is cost effective but more expensive than PS, PVC, or PETG. Common industries and uses include: POP displays, signs, tool cases, automotive applications, consumer goods, storage trays, storage cases.