A great way to upgrade your packaging is through high quality print design. It can turn an average looking box into a unique and beautiful package. Great packaging print and logos can help distinguish a brand and catch the eye of the consumer from the shelf. There are many different methods of printing that can that you can use to achieve your desired look. How do you decide which method is best to use? There are three primary methods – Lithography, Flexography, and Digital Print. In this article, I will walk you through each printing method’s pros and cons so you can choose what is best for your needs.
Let’s begin with Flexography.
What is flexographic printing?
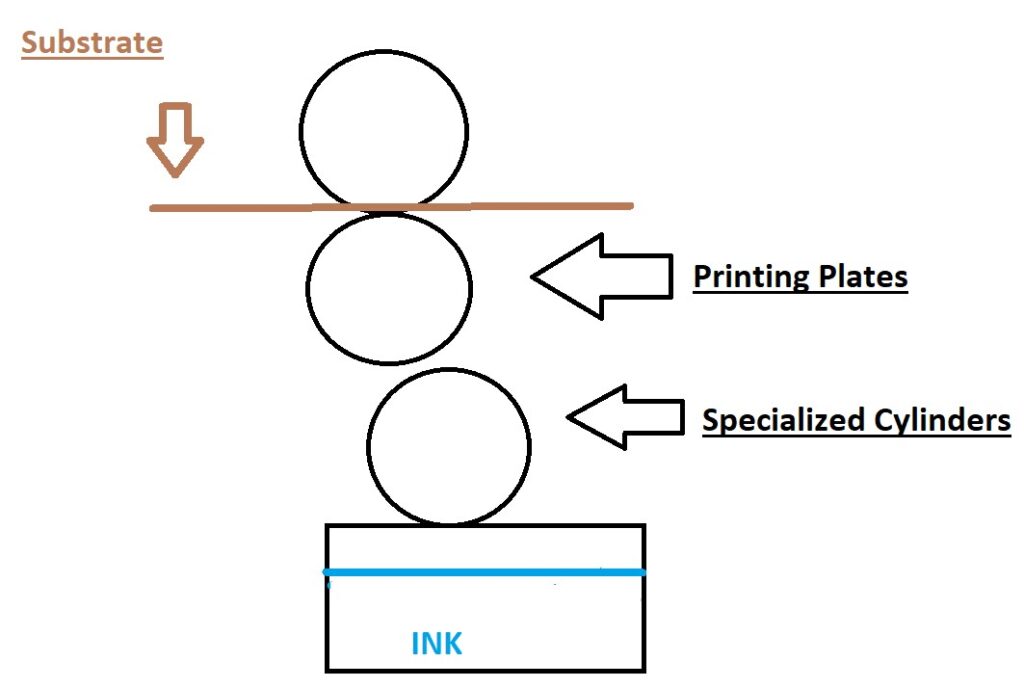
In simple terms, you can think of Flexographic or “Flexo” printing like a giant rubber stamp. This print design method uses flexible printing plates that are wrapped around specialized cylinders. These cylinders pick up the ink and apply it to the printing medium or “substrate”. The printing plates have a raised image embedded on them and as the substrate moves through the machine the printing plates then transfer or “stamp” the image with quick drying ink onto the substrate. Each printing plate has its own color, so as the substrate continues through the machine across multiple printing plates, more colors get added. Once the machine is set up, the process can move very quickly which makes this a very efficient printing method for high volume jobs.
What are the advantages & disadvantages to this method?
Advantages:
- Highly efficient / fast = higher cost
- Large orders / long runs versions
- Prints directly on unique substrates
- Suited for continuous patterns
Disadvantages:
- Printing plate cost: more colors
- Expensive for multiple print
- High initial start-up costs
When is it best to use flexographic printing?
Flexographic printing is a highly efficient method of printing. You can complete all of the typical printing and design processes through one passage of the machine. This makes flexo printing ideal for large orders and long runs. This method also can print on a wide variety of different materials including paper, plastic, corrugated, etc. so if you have a project that uses a unique material this method may be the best fit for you. It does take some time to set up the machine, so you should try and have limited print versions or focus on continuous pattern / image. If you are wanting numerous different print versions, you may want to choose one of the other printing methods I talk about below which offer more versatility in print style and modification.
Let’s move on to Lithography.
What is lithographic printing?
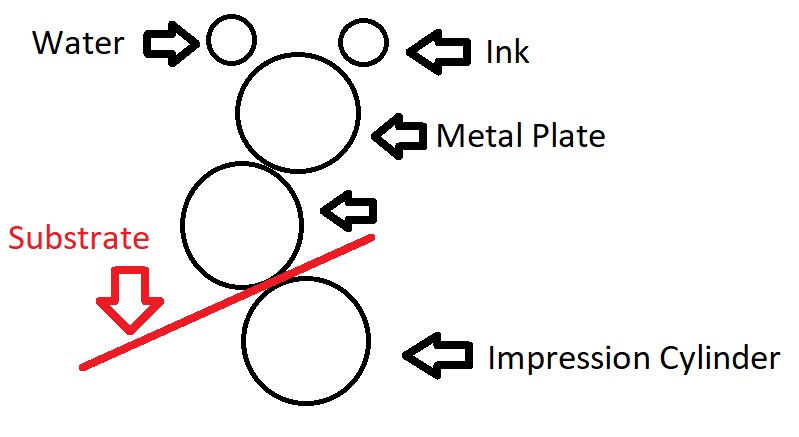
Lithography uses a mix of oil-based ink and water to apply an image to a substrate. The ink and water are combined on a metal “printing plate” first to get the initial coloring and pattern down. Then, the image is transferred to a synthetic rubber mat also known as the “rubber blanket” which applies the final design to the product. The rubber blanket does the actual printing onto the substrate in a continuous fashion. The result is a very crisp image that can be replicated quickly and accurately by re-applying ink and water to the metal print plate rather than the entire print die or “rubber blanket”.
Lithography typically only works for smooth, flat surfaces. If you have a surface that is coarse like corrugated, then an additional process called lithographic lamination is likely needed. With lithographic lamination, the image first gets applied to a liner board or paper, which is then attached to the corrugated. You can think of this like a high-end label for your corrugated product.
What are the advantages & disadvantages?
Advantages:
- High quality sharp images
- Large orders
- Can accommodate embellishments
- Inexpensive printing plates
Disadvantages:
- Does good for rough surfaces
- Sometimes higher cost
- More sensitive to cracking on certain surfaces
When is it best to use lithographic printing?
Lithography is best to use on flat surfaces and larger print runs. It is great for magazines, books, folding cartons, and many other printed items when high detail and crisp images are desired.
Let’s finish with Digital printing.
What is digital printing?
Digital printing is one of the newer methods of printing. It works very similarly to the typical printer you would use in an office. The image is created digitally on a computer and with ink and heat the image gets printed directly onto the substrate. It doesn’t involve any printing plates or in-depth manufacturing processes. Print jobs can be changed on the fly with little additional cost. The overall printing does take longer because of the digital process, so this is more geared towards smaller runs or variable printing. This technology is continuously improving; some experts in the industry believe all print will eventually shift to digital.
What are the advantages & disadvantages?
Advantages:
- No Printing plates needed
- Relatively high-quality image
- Cost effective small volume production
- Low setup costs
Disadvantages:
- Limited price breaks
- Slow production speed
- Limited embellishments
When is it best to use Digital printing?
Digital printing is best suited for short run, flexible projects. It is a great option if you need your product done in a quick time frame and are on a budget. Digital printing is also great when you need to make an adjustment to your print job on the fly, since it does not require new plates like flexography and lithography would. Things like small batch flyers, brochures, business cards, and more would be a good fit for digital printing.
Which method of printing should I choose for my project?
There is no correct answer to this question. Each project should be reviewed to determine the best printing method. Print projects can involve just one of these processes, or a combination depending on the scope and your needs. Evaluate the project priorities and determine which method would suit your project best. Contact PAX Solutions today for help with your next print project.